Political cartoons have a long and fascinating history, serving as a powerful tool for satire, social critique, and political commentary. These illustrations have evolved significantly over time, influencing public opinion, shaping political discourse, and even sparking movements. Let’s explore the origins, development, and global impact of political cartoons throughout history.
1. Origins of Political Cartoons
Political cartoons date back centuries, though their modern form began taking shape in the 18th century. Early examples can be found in the works of satirists and artists who used visual humor to critique politics, society, and leaders.
- Ancient Times: The roots of political cartoons can be traced back to ancient civilizations like Ancient Egypt, where satirical illustrations and caricatures of leaders were used to mock or criticize their rule.
- 17th and 18th Centuries: The first recognizable political cartoons emerged in Europe, particularly in England, where artists such as James Gillray and George Cruikshank used caricature and humor to lampoon political figures.
- The Birth of Modern Political Cartoons: In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the development of lithography and engraving allowed for mass production of illustrations, which made political cartoons more widely accessible.
2. The Role of Political Cartoons in Revolutionary Movements
During times of social upheaval and political revolutions, political cartoons have played a significant role in mobilizing public opinion and encouraging change.
- French Revolution: Political cartoons were instrumental during the French Revolution, with satirists mocking the monarchy and the aristocracy. They helped fuel the anger of the people and spread revolutionary ideas.
- American Revolution: In the United States, cartoons helped galvanize public support for independence. For example, Benjamin Franklin’s famous “Join, or Die” cartoon, which depicted a segmented snake, became a symbol of colonial unity.
- Anti-Colonial Movements: Political cartoons have often been used to criticize colonial powers, offering visual critiques of oppression and exploitation. In many parts of the world, they served as a tool for resistance and activism.
3. Political Cartoons in the 19th and 20th Centuries
As the printing press advanced and newspapers became more widespread, political cartoons grew in prominence and sophistication.
- The Golden Age of Political Cartoons: The 19th century saw the rise of iconic political cartoonists such as Thomas Nast in the United States and Sir John Tenniel in England. Nast’s cartoons, for example, helped shape American politics, particularly his work in exposing political corruption, including his role in the downfall of political boss William “Boss” Tweed.
- Influence of Technology: The advent of photography and color printing in the early 20th century expanded the reach of political cartoons. Newspapers could now print in full color, allowing cartoonists to create more striking and detailed works.
- World Wars: During both World War I and II, political cartoons became a crucial part of wartime propaganda, serving to promote nationalism, vilify enemies, and boost morale. Cartoons were an effective means of communicating complex political messages to large audiences in a quick and understandable format
4. Political Cartoons in the Global Context
Political cartoons have not only been a tool of commentary in Western nations but have also played significant roles in other regions worldwide.
- Latin America: In Latin America, political cartoons have often been used to critique authoritarian governments and foreign influence. Cartoonists have been instrumental in critiquing military dictatorships, corruption, and social inequality.
- Asia and Africa: In countries like India, Japan, and South Africa, political cartoons have served as a means to challenge colonialism, oppressive regimes, and social injustices. For example, during apartheid in South Africa, cartoons played a crucial role in critiquing the oppressive system.
- Global Impact of Satirical Cartoons: The spread of political cartoons in global media has meant that they now address universal themes such as human rights, inequality, and corruption. With the rise of social media, these cartoons now circulate globally, transcending national borders and impacting international conversations.
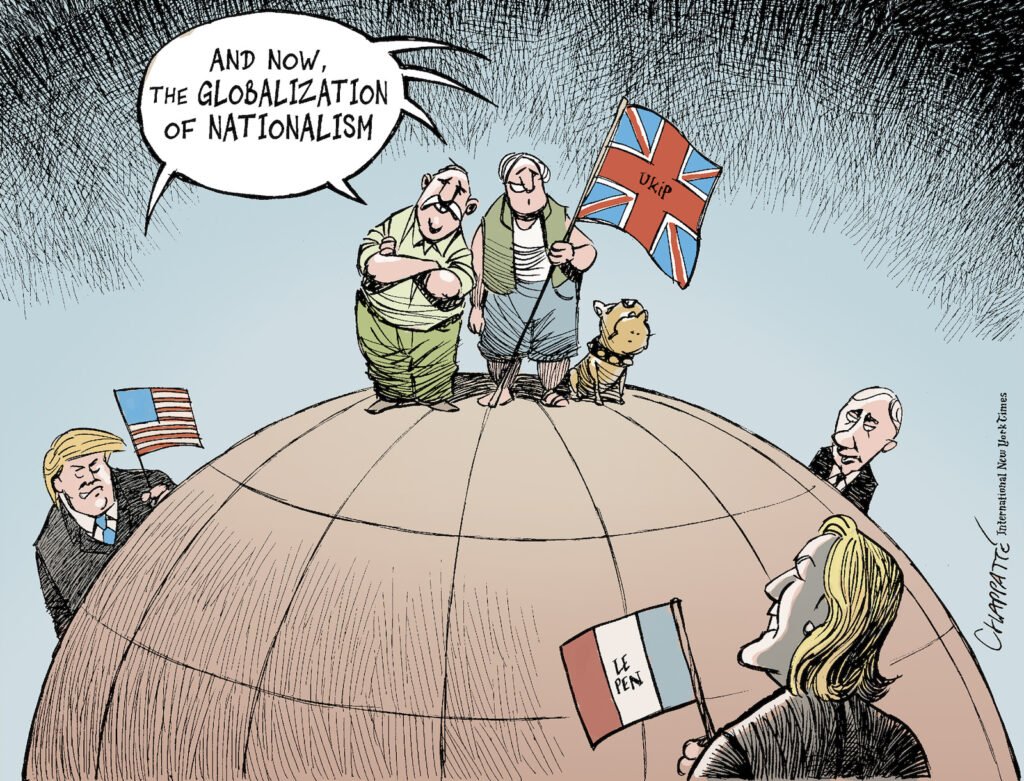

5. The Influence of Political Cartoons on Public Opinion
Political cartoons have a unique ability to shape public opinion and influence political outcomes. Their combination of humor, satire, and illustration allows them to convey complex messages in a digestible and impactful way.
- Challenging Authority: Political cartoons have often been used to challenge those in power, providing a voice for the marginalized and holding leaders accountable.
- Raising Awareness: Cartoons often highlight social issues, helping to raise awareness about important causes and encouraging social change.
- Fostering Dialogue: By presenting controversial issues in a humorous or exaggerated manner, political cartoons prompt discussions and debates that may not otherwise take place.
6. The Role of Political Cartoons in the Digital Age
In the 21st century, the internet has had a profound impact on the world of political cartoons.
- Viral Cartoons: With the rise of social media, political cartoons can spread like wildfire, reaching a global audience in a matter of hours.
- Digital Satire: Cartoonists now use digital tools to create more polished and interactive content. Animated cartoons and meme-based satire have become dominant forms of political humor.
- Citizen Cartoonists: The democratization of digital media means that anyone with an internet connection can create and share political cartoons, adding to the diverse range of perspectives.
7. The Future of Political Cartoons
As the media landscape continues to evolve, the role of political cartoons is also changing.
- Adapting to New Media: Political cartoons are increasingly being produced for digital platforms, such as blogs, social media, and news websites, allowing them to reach younger and more diverse audiences.
- New Forms of Expression: The rise of interactive media, augmented reality, and digital animation offers new avenues for political cartoonists to explore.
- Continued Relevance: While the format may change, political cartoons will likely remain an essential form of political commentary. They have proven their adaptability, surviving through centuries of social and technological changes.
Conclusion
The history of political cartoons is a testament to the power of visual storytelling in shaping public opinion, challenging authority, and inspiring change. From their origins in 18th-century Europe to their global impact today, political cartoons continue to influence society and politics worldwide. As we move further into the digital age, their role in informing, entertaining, and mobilizing the public remains as relevant as ever.